Immunity And Types

Immunity And Types
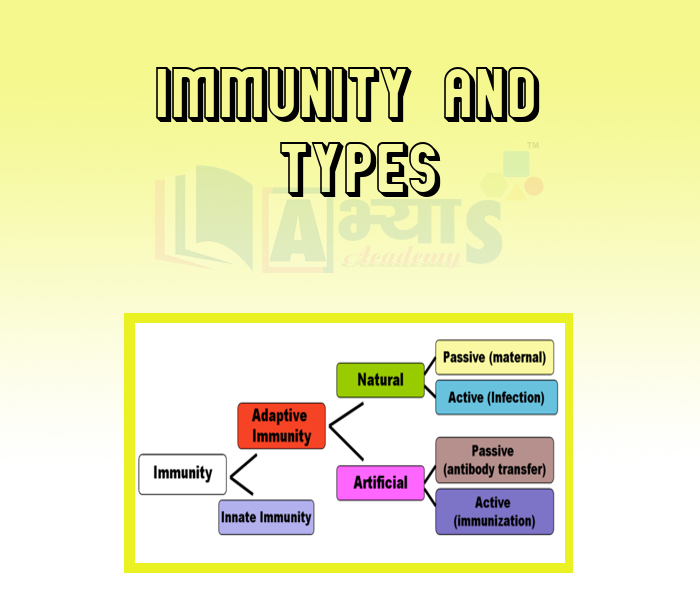
The ability of the body (host) to fight against the disease causing agent is called immunity. It is of two types:-
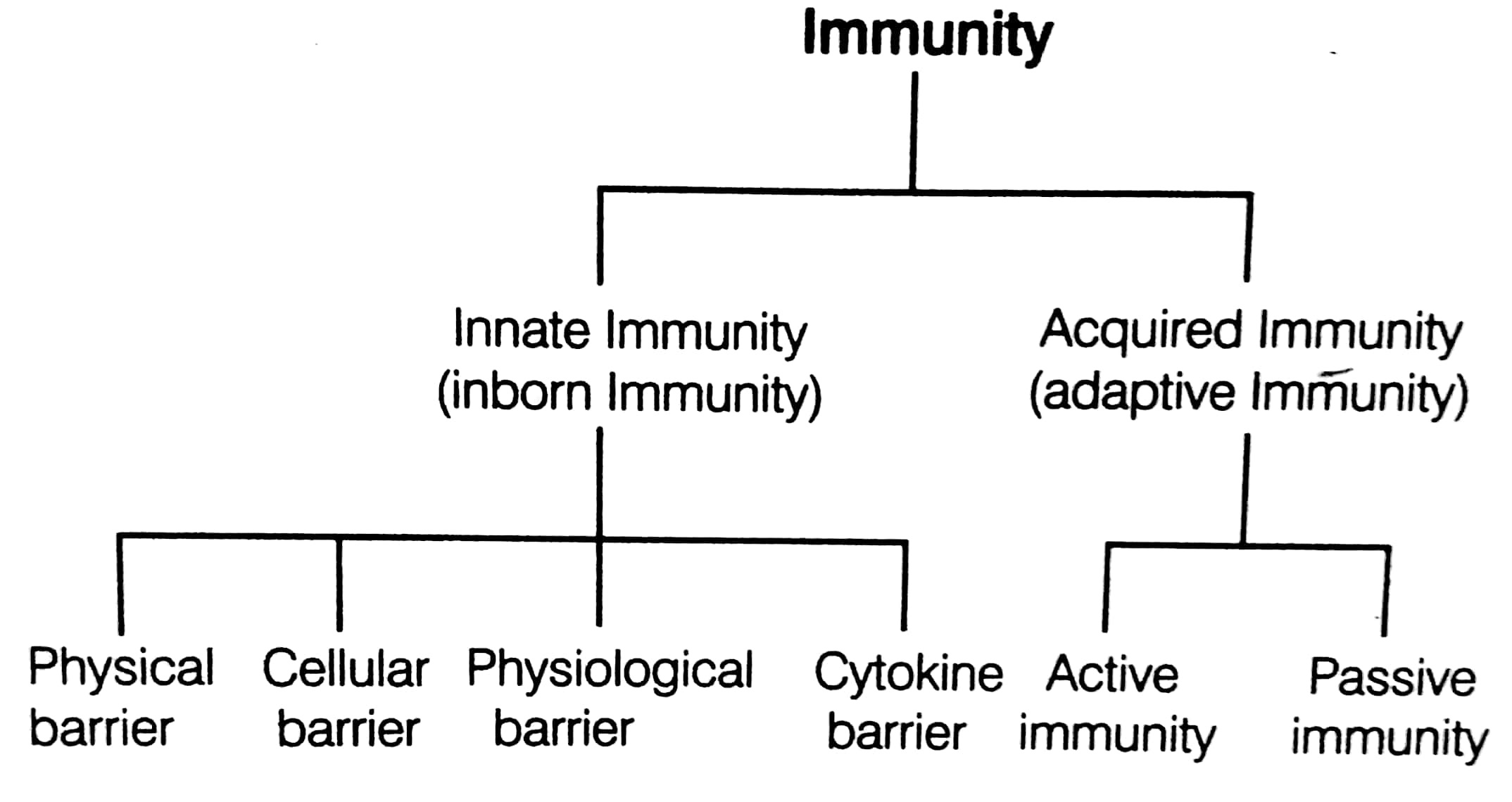
(1) Innate Immunity :
It refers to all the defense elements with which an individual is born and always available to protect the body. It is a non-specific type of defense system.
(i) It is present from the time of birth and inherited from parents.
(ii) It consists of four types of barrier system that prevent the entry of pathogen or foreign element into the body.
Types of Barriers in Innate Immunity:-
Various types of barriers are as follows :-
(i) Physical Barriers Skin is the first line of defense :- It prevents the entry of the pathogens of the body. Mucus coating of the epithelium lining the respiratory, gastrointestinal and urogenital tracts also help in trapping microbes.
(ii) Physiological Barriers :- Acid in the stomach, saliva in the mouth, tears from the eyes, etc., prevent the growth of microbes.
(iii) Cellular Barrier :- Special types of cells in our body, which kill the disease causing agents. Example are WBCS, (leukocytes) Polymorpho Nuclear Leukocytes (PMNL-neutrophils, monocytes, macrophages, etc.)
(iv) Cytokine Barrier Cells which are virus-infected, release types of protein called interferons. Interferons the uninfected cells from further infection.
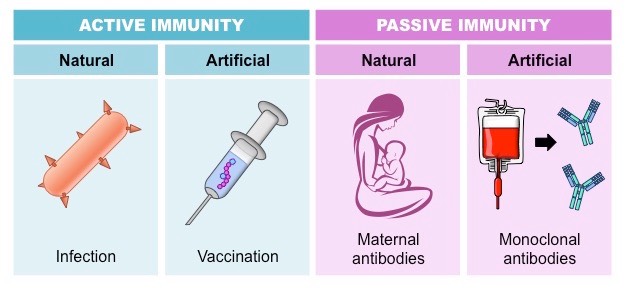
(2) Acquired Immunity
It is pathogen specific and is not present from the birth and develops during an individual's lifetime.
This type of immunity is acquired after the birth, either by contracting the disease or by vaccination.
It has the following characters :-
(i) Specificity :-It has the ability to distinguish many different foreign molecules accordingly.
(ii) Memory :- It is a unique feature, which helps in producing an intensive response when the pathogen attacks the second time.
Students / Parents Reviews [10]
A marvelous experience with Abhyas. I am glad to share that my ward has achieved more than enough at the Ambala ABHYAS centre. Years have passed on and more and more he has gained. May the centre flourish and develop day by day by the grace of God.

Archit Segal
7thAbout Abhyas metholodology the teachers are very nice and hardworking toward students.The Centre Head Mrs Anu Sethi is also a brilliant teacher.Abhyas has taught me how to overcome problems and has always taken my doubts and suppoeted me.

Shreya Shrivastava
8thIt was a good experience with Abhyas Academy. I even faced problems in starting but slowly and steadily overcomed. Especially reasoning classes helped me a lot.

Cheshta
10thMy experience with Abhyas academy is very good. I did not think that my every subject coming here will be so strong. The main thing is that the online tests had made me learn here more things.

Hiya Gupta
8thAbhyas is a complete education Institute. Here extreme care is taken by teacher with the help of regular exam. Extra classes also conducted by the institute, if the student is weak.

Om Umang
10thOne of the best institutes to develope a child interest in studies.Provides SST and English knowledge also unlike other institutes. Teachers are co operative and friendly online tests andPPT develope practical knowledge also.

Aman Kumar Shrivastava
10thIt has a great methodology. Students here can get analysis to their test quickly.We can learn easily through PPTs and the testing methods are good. We know that where we have to practice

Barkha Arora
10thIt was good as the experience because as we had come here we had been improved in a such envirnment created here.Extra is taught which is beneficial for future.

Eshan Arora
8thAbhyas Methodology is very good. It is based on according to student and each child manages accordingly to its properly. Methodology has improved the abilities of students to shine them in future.

Manish Kumar
10thBeing a parent, I saw my daughter improvement in her studies by seeing a good result in all day to day compititive exam TMO, NSO, IEO etc and as well as studies. I have got a fruitful result from my daughter.
